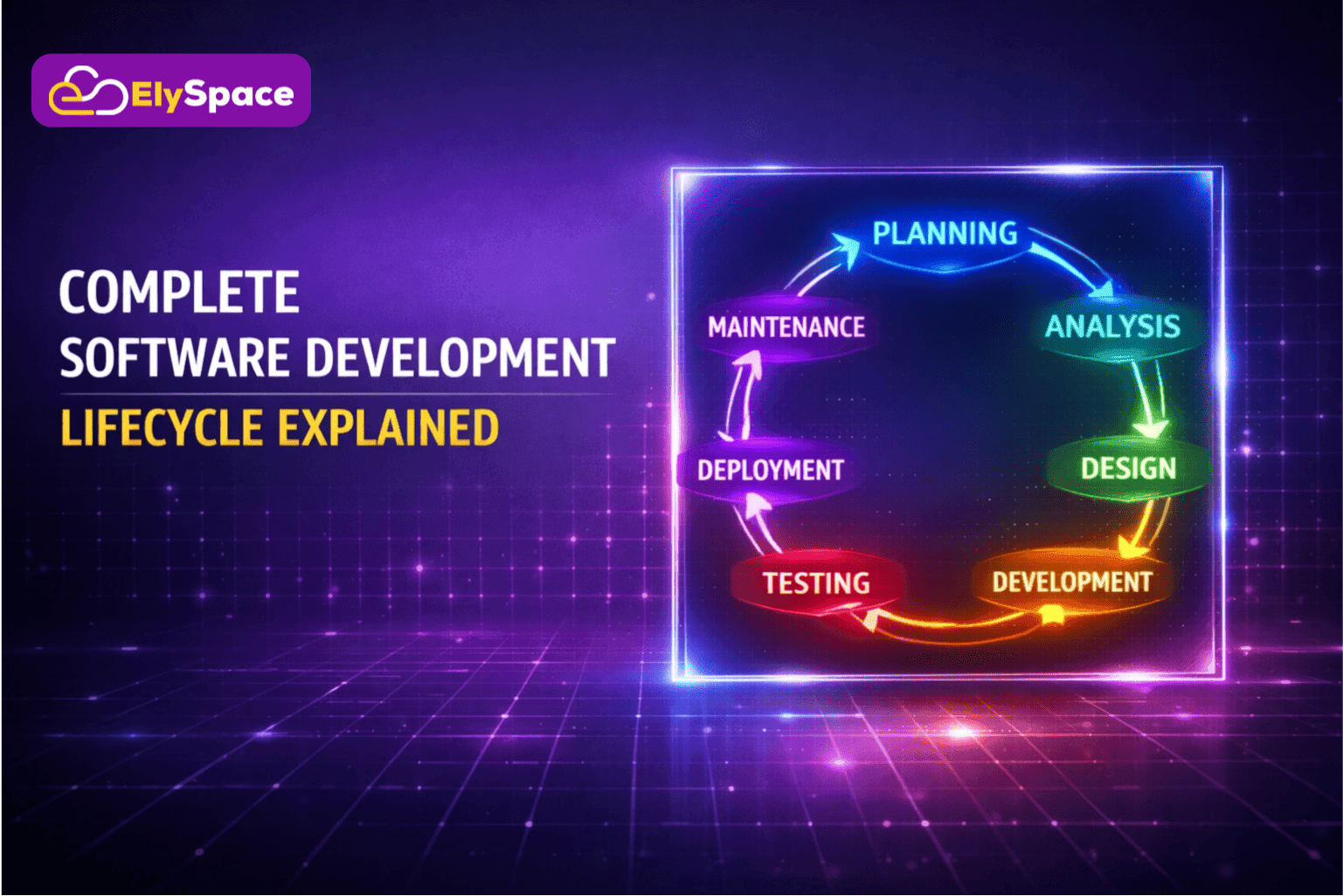
What does “software development lifecycle” simply mean? It is the process that turns your business idea into functional software. Whether it is an enterprise system, web platform, or mobile app, the software development lifecycle decides the success or failure of your project.
The process of developing custom software follows a set of tried and true steps that ensure risks are kept to a minimum level and quality is maximized. This complete blog will walk you through each step of the way so you know exactly how companies utilize custom software to meet their real world goals.
What Is the Software Development Lifecycle?

Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) is a structured approach that helps in planning, developing, testing, and deploying software applications. SDLC ensures that the software development process remains organized and meets the desired quality standards.
Consider the software development lifecycle as a roadmap. Just like building projects use blueprints, software projects have stages that need to be completed from initial concept to completion.
Organizations apply the SDLC to ensure the costs remain under control, the timelines are managed, and the software produced is trustworthy and solves the problems of the users. Without the SDLC, the process of software development becomes disorganized, and the costs become unmanageable.
Why SDLC Matters for Businesses

Cost Control and Predictability
A clear understanding of the SDLC process reveals where exactly the funds and manpower are allocated in every phase. If you properly utilize SDLC, you can reduce development costs by up to 20-40% by not rushing through the development in an unorganized way.
Quality Assurance
During custom software development process, when you do quality testing, it simply allows bugs to be corrected when they are least expensive to repair. According to IBM’s software development study of structured SDLC processes, post deployment defects can be fixed and reduced by as much as 60%.
Risk Management
When you trace out where this new software will really be used in the business in your overall SDLC, you can identify problems in development early when structured life cycles are followed.
The 7 Essential SDLC Phases Explained
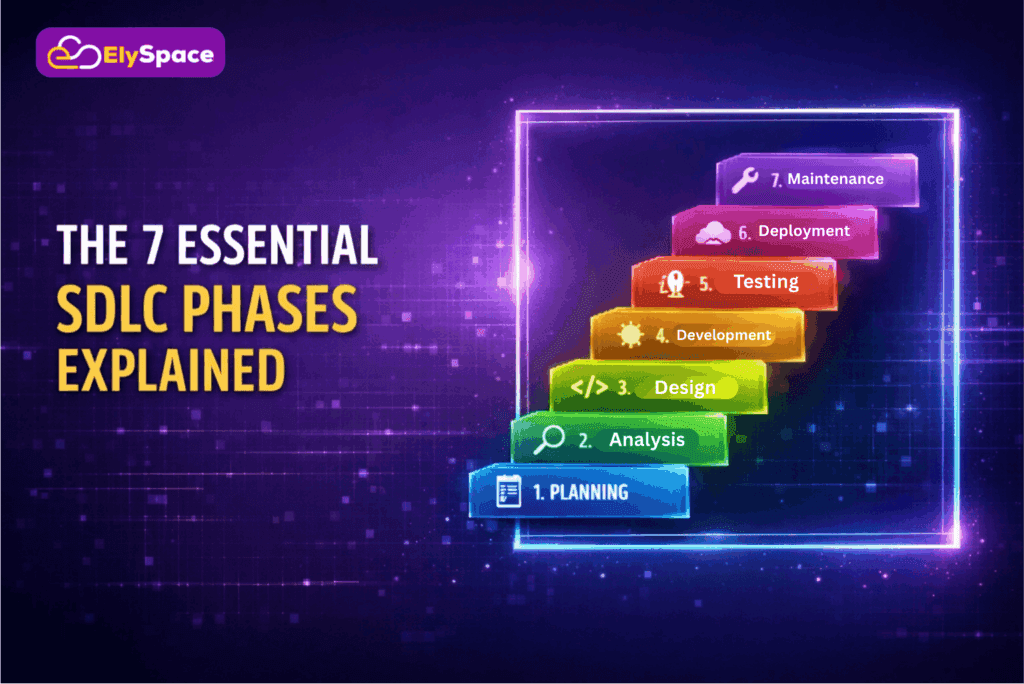
Phase 1: Planning and Requirement Analysis
This phase is the foundation phase that establishes what your software will do and why it is important. Business analysts collect requirements from stakeholders on specific functionalities, performance, and user experience.
The planning phase of projects defines the scope of the project, thereby avoiding feature creep (uncontrolled addition of new features), which increases the cost of projects. The teams perform feasibility studies, which include technical capabilities, operational requirements, and economic feasibility.
Feasibility: the state or degree of being easily or conveniently done.
Phase 2: System Design and Architecture
The fundamentals of software architecture are relevant during design cycles. This is where the team takes the requirements and creates a technical design that illustrates how the components interact to meet business needs.
The architects choose the most appropriate technology stack, database, and frameworks. They design system interfaces, data structures, and security protocols that make software scalability understandable through foundation planning.
Cloud based software becomes relevant in this context as teams consider on premise, cloud, or hybrid models. Such considerations have a significant impact on costs, scalability, and maintenance.
On premise: means owning and managing your own servers (full control, high upfront cost).
Cloud: means using a third party provider’s servers (pay-as-you-go, easy scaling, less control).
Hybrid: blends both, keeping sensitive data on premise while leveraging cloud scalability for other workloads, offering flexibility but with added complexity
Phase 3: Development and Implementation
The actual coding is done by the developers based on the approved designs. The modern custom software development process follows modular coding (breaking a large program into smaller, independent, reusable blocks called modules), where the developers create independent components/modules that integrate smoothly.
Version control systems, such as Git, record all changes made to the code, making it possible to collaborate on the code without conflicts. The benefits of custom software for businesses are realized during the development process, where custom software is altered to address certain business processes.
Phase 4: Testing and Quality Assurance
Complete testing ensures that the software works as expected under different conditions. The QA (Quality Assurance) teams perform unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing.
The use of automated testing tools, such as Selenium from providers, pushes this process while ensuring that it is handled with great care and attention. Testing helps to identify flaws, performance problems, security holes, and usability problems before users experience them.
Phase 5: Deployment and Release
Deployment is moving the software from the “workshop” where it was built to the “real world” where people actually use it. Teams plan this carefully so the software doesn’t break or stop working when it launches.
Cloud based tools use “containers” (like digital boxes) to make sure the software works the same way for everyone. This helps businesses update their technology quickly and easily without any hiccups.
Phase 6: Maintenance and Support
After deployment, software undergoes maintenance to fix bugs, performance problems, and requests for new features. This phase usually takes up 60-80% of the total cost of software over its lifetime.
Business automation using software needs proper maintenance to ensure that the software runs all the time.
Phase 7: Evaluation and Iteration
The software development lifecycle is described in terms of circular, rather than linear, which represents the idea of continuous improvement. The process of gathering user feedback, analyzing performance metrics, and finding areas for improvement is part of this.
This feedback and need for improvement leads to another development cycle, which takes the software to a better level. The scalability of software, described through iterative improvement, enables systems to expand with businesses.
Popular Software Development Models
Waterfall Model:
The waterfall model proceeds with each phase one after the other before moving ahead. The requirements go through design, development, testing, and implementation in a sequential manner.
Best For: Projects with well defined, stable requirements.
Advantages: Well defined milestones, well documented, easy to manage
Limitations: Inflexible when requirements change, testing postponed until late stages.
Agile Methodology
Agile development focuses on iterative development in short cycles called sprints. The agile team delivers working software incrementally while responding to changing requirements.
The process of developing custom software is greatly aided by the flexibility offered by Agile. When businesses find new requirements, Agile teams are able to shift priorities quickly.
Best For: When requirements change or feedback from users influences development.
Advantages: Quick response to change, continuous delivery, risk minimized by incremental approach.
DevOps Model
DevOps is the integration of development and operations, with a focus on automation, continuous integration, and quick releases. This is helpful for business automation via software because it allows for quick and reliable releases.
Best For: Organizations that value speed, automation, and reliability.
Knowledge about the usage of custom software by businesses is essential in deciding the best model to adopt. Enterprise software may need the documentation of waterfall while customer facing software may benefit from the agility of Agile.
Custom Software Development Best Practices

1. Prioritize Clear Communication
Challenges and solutions for successful software development begin with communication. Holding regular meetings with stakeholders helps keep everyone on the same page.
2. Document Everything
Documentation assists in maintenance tasks and ensures knowledge continuity. Document requirements, architecture decisions, APIs, and deployment.
3. Implement Automation
Automation minimizes the possibility of human error while speeding up delivery. Regressions are automatically detected by automated testing, and approved changes are automatically deployed through continuous deployment pipelines.
The benefits of custom software for businesses can be multiplied when automation is used to perform repetitive tasks, allowing developers to focus on more valuable tasks.
4. Plan for Scalability
What is software scalability? It is designing systems that can grow without having to completely rewrite them. Cloud based software benefits include elastic scaling, where resources scale based on demand.
5. Integrate Security Throughout
Security cannot be an afterthought. Incorporate security reviews, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing throughout the software development lifecycle phases.
6. Collect Continuous Feedback
Feedback from users brings about positive changes. Digital transformation via software is a success if technology is used to enhance user experiences.
Software Development Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Scope Creep
Uncontrolled feature addition raises the costs and delays delivery. Stakeholders keep on requesting changes that, with time, sum up into major scope expansion.
Solution: Make your change management processes strict. Evaluate new requests against the project goals and postpone nonessential features to future releases.
Challenge: Technical Debt
Quick fixes pile up and then create maintenance nightmares. Code becomes weak, and performance decreases over time.
Solution: Make time for refactoring during each sprint. Pay down technical debt in small installments instead of allowing it to build up.
Challenge: Complexity of Integration
Custom software doesn’t live in isolation mostly. Integrations with existing systems or third party APIs add surprising complexity.
Solution: Perform integration testing early. Create adapters and abstraction layers to separate your code from any external dependencies.
Challenge: Resource Limitations and Restrictions
It forces hard trade offs (compromises) between quality and features with delivery speed because of budget limitations, skill gaps, and timeline pressures.
Solution: Partner with experienced development firms that provide flexible engagement models. Choose a team that increases your capabilities with specialized skills exactly when required.
Choosing the Right SDLC Approach

Evaluate Project Characteristics
Think about the size, complexity, and length involved in your project as well as whether it is on a smaller scale; if it is, then the requirements can easily be met through a waterfall type of methodology.
But it is larger and can change with time, so understand requirements very well before you begin; projects having low certainty are a natural fit for an iterative model.
Consider Team Structure
Distributed teams also demand good documentation and tools that facilitate communication when team members are not in sync. Assessment of team expertise in different methodologies should be done prior to commitment.
Evaluate Business Limitations and Restrictions
The degree of budget flexibility can influence model selection. Fixed price contracts may align more closely with waterfall’s predictability, whereas a project that may require changes with time that can’t be predicted currently better matches Agile’s flexibility.
The advantages that custom software brings to businesses include “aligning with particular business processes.” Stakeholder engagement is always needed, regardless of methodology.
Why Partner with ElySpace
ElySpace specializes in custom software development, from initial product plans all the way through maintenance. We have a team of expert developers, who use effective development methodologies for many clients.
We’re aware of the ways by which businesses utilize customized software to obtain competitive advantages. We follow a software development approach that highlights the importance of collaboration, transparency, and tangible business value.
Our Services Include:
- Custom Software Development: Developing software solutions with state-of-the-art technology and application of software architecture principles in order to guarantee their scalability
- Web Development: Responsive, performance driven interactive applications
- Cloud Solutions: Cloud based software and its practical applications on AWS and Azure
- Domain and Hosting: Infrastructure with Great Performance and Uptime
Visit ElySpace to have your software development requirements discussed under free consultations.
Conclusion
The basis for successful software projects is provided by the software development lifecycle. You can make wise decisions if you are aware of these stages, models, and best practices.
The success of the custom software development process depends on selecting the right approaches, keeping lines of communication open, and concentrating on providing business value. With careful planning and knowledgeable direction, software development problems and solutions become manageable.
Software scalability, which is explained by appropriate architecture, guarantees that your investment will continue to yield returns as your company expands. In today’s markets, software driven digital transformation and business automation are essential for competitiveness.
Are you prepared to use custom software to revolutionize your company? Get in touch with ElySpace right now to start your journey toward software that resolves your issues and produces quantifiable outcomes.